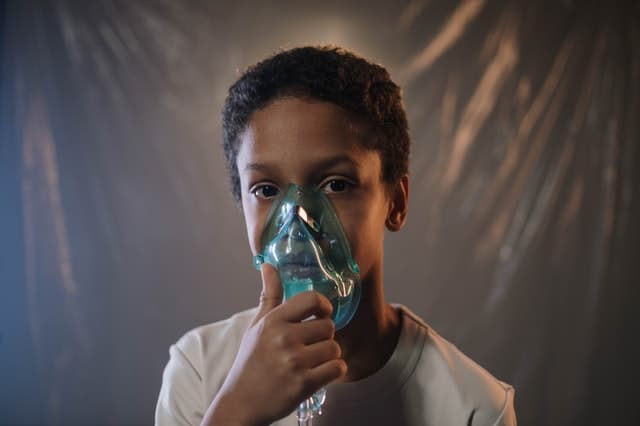INHALATION OF FUMES The inhalation of smoke, gases [such as carbon monoxide) or toxic vapours can be lethal. A casualty who has inhaled fumes is likely to have low levels of oxygen in his body tissues [Hypoxia p 90) and therefore needs urgent medical attention. Do not attempt to carry out a rescue if it is likely to put your own life at risk; fumes that have built up in a confined space will quickly overcome anyone who is not wearing protective equipment. SMOKE INHALATION Any person who has been enclosed in a confined space during a fire should be assumed to have inhaled smoke. Smoke from burning plastics, foam…
-
-
What Causes an Airway Obstruction.
What is an airway obstruction? In the airway obstruction may be a blockage in any a part of the airway. if airway may be a complex system of tubes that conveys inhaled air from your nose and mouth into your lungs. An obstruction may partially or totally prevent air from stepping into your lungs. Some airway obstructions are minor, while others are life-threatening emergencies that need immediate medical attention. Types of airway obstructions The types of airway obstructions are classified supported where the obstruction occurs and the way much it blocks. Airway Obstructions Recognition The airway may be obstructed externally or internally, for example, by an object that is stuck…
-
FIRST AID: Choking Symptoms and Treatment
What do you have to do if an individual is choking but remains ready to speak or breathe? What is choking and how is it happen? This condition arises when there’s insufficient oxygen within the body tissues. There are a variety of causes of hypoxia, starting from suffocation, choking, or poisoning to impaired lung or brain function. The condition is amid a spread of symptoms, counting on the degree of hypoxia. If not treated quickly, hypoxia is potentially fatal because of a sufficient level of oxygen. is significant for the traditional function of all the body organs and tissues, but especially the brain. In a healthy person, the quantity of…
-
HOW TO USE AN AED
How to use an AED, When the heart stops, a cardiac arrest has occurred. The most common cause is an abnormal rhythm of the heart, known as ventricular fibrillation. This abnormal rhythm can occur when the heart muscle is damaged because of a heart attack or when insufficient oxygen reaches the heart. A machine called an automated external defibrillator [AED] can be used to correct the heart rhythm by one or more electric “shocks··. AEDs are available in many public places, including shopping centers, railway stations, and airports. The machine analyses the casualty’s heart rhythm and shows with visual prompts – or tells you by voice prompts – what action…
-
RESUSCITATION UNCONSCIOUS CHILD
The following describes the techniques that may be needed for the resuscitation of an unconscious child aged between one year and puberty. When treating a child, always approach and treat her from the same side, kneeling down next to the head or chest. You will then be in the correct position to carry out all the different stages of resuscitation: opening the airway, checking to breathe, and giving rescue breaths and chest compressions (together known as cardiopulmonary resuscitation, or CPR) At each stage you will have decisions to make, for example, is the child breathing? The steps are given here tell you what to do next. Your first priority is…
-
FIRST AID – SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR CPR
SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR CPR How to CPR is There are circumstances when it may be more difficult to deliver CPR; for example, a casualty may have a chemical around the mouth, in which case you can give rescue breaths through the nose [opposite]. Occasionally, a casualty may breathe through a hole in the front of the neck – a stoma -[opposite]. You can also use a pocket mask or face shield when giving rescue breaths. If you have help, one person can perform full cycles of CPR for two minutes, then a second person can take over. Continue to swap every two minutes. PROBLEMS WITH RESCUE BREATHING If a casualty’s…
-
HOW TO MANAGING UNCONSCIOUS ADULTS
Here we describe techniques for the management of an unconscious adult who may require resuscitation. Always approach and treat the casualty from the side, kneeling down next to his head or chest. You will then be in the correct position to perform all the stages of resuscitation: opening the airway; checking to breathe and giving chest compressions and rescue breaths (together called cardiopulmonary resuscitation, or CPR) At each stage in the process you will have decisions to make, for example, is casualty breathing? The steps are given here tell you what to do next. The first priority is to open the casualty’s airway so that he can breathe or you…