How many types of bleed injuries are there?
Types of Wounds, When a blood vessel is damaged, the vessel constricts, and a series of chemical reactions occur to form a blood clot -a plug’ over the damaged area (below). If large blood vessels are torn or severed, uncontrolled blood loss may occur before clotting can happen, and shock may develop.
TYPES OF WOUND BLEEDING
Bleeding [hemorrhage) is classified by the type of blood vessel that is damaged. Arteries carry oxygenated blood under pressure from the heart. If an artery is damaged, bleeding will be profuse. Blood will spurt call at the time with the heartbeat.
If the main artery is severed, the volume of the Circulating heard Will fad rapidly Blood from veins, having given up its oxygen into the tissues, is a darker red.
It is under less pressure than arterial blood. but vein walls can widen greatly and therefore the blood can “pool” inside them [varicose vein).
If a large or varicose vein is damaged. blood will gush from It profusely. Bleeding from capillaries occurs with any wound. At first, bleeding (‘lay be brisk, but blood loss is usually slight. A blow may rupture capillaries under the skin, causing bleeding into the tissues [bruising).
HOW WOUNDS HEAL
When a vessel is severed or damaged, it constricts (narrows) so as to stop excessive amounts of UI blood from escaping. Injured tissue cells at the location of the wound, together wi h specialized blood cells called platelets, then trigger a way of chemical reactions that end in the formation of a substance that forms a mesh.
This mesh traps blood cells to form a grume. The clot releases a fluid referred to as a serum, which contains antibodies and specialized cells; this serum begins the method of repairing the damaged area,
At first, the grume may be a jelly-like mass. Fibroblast cells from a plug within the clot. Later, this dries into a crust (scab) that seals and protects the location of the wound until the healing process is complete.
What are the 3 types of wound healing?

Injury
At the site of injury, platelets in the blood arrive to begin the formation of a clot. Other cells are attracted to the site to help with the repair.

Clotting
A clot is formed by platelets in the blood and blood-clotting protein, Tissue-forming cells migrate to the damaged area to start repair.

Plugging and scabbing
A plug of fibrous tissue is formed within the clot The plug hardens and forms a scab that eventually drops off when the skin beneath it is healed.
What are the types of wounds?
Wounds are often classified into a variety of various types, counting on the thing that produces the wound – like a knife a bullet – and therefore the manner during which the wound has been inflicted. Each of those sorts of wounds carries specific risks related to surrounding tissue damage and infection.
- Incised wound
- Laceration wound
- Abrasion wound
- Puncture wound
- Continues(BRUISE) wound
- Stab wound
- Gunshot wound
Let’s see each of the wound types for more details:

INCISED WOUND
This is caused by a clean surface cut from a sharp-edged object such as a razor. Blood vessels are cut straight across, so bleeding may be profuse. Structures such as tendons or nerves may be damaged.
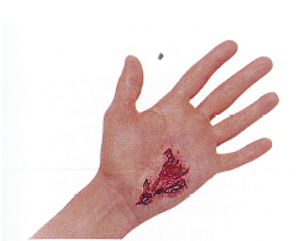
LACERATION
Crushing or ripping forces result in tears or lacerations. These wounds may bleed profusely than incised wounds. but there is likely to be more tissue damage. Lacerations are often contaminated with germs, so the risk of infection is high.

ABRASION (GRAZE)
This is a superficial wound in which the topmost layers of skin are scraped off, leaving a raw, tender area. Abrasions are often caused by a sliding fall or a friction burn. They can contain embedded foreign particles that may cause infection.
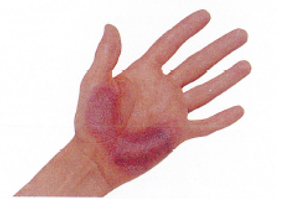
CONTUSION (BRUISE)
A blunt blow can rupture capillaries beneath the skin. causing blood to leak into the tissues. This process results in bruising. The skin may also split. Extensive contusion may indicate deeper damage, such as a fracture or an internal injury.

PUNCTURE WOUND
An injury such as standing on a nail or being pricked by a needle will result in a puncture wound. It has a small entry site but a deep track of internal damage. Since germs and dirt can be carried far into the body, the infection risk with this kind of wound is high.

STAB WOUND
This type of wound can be caused by a long or bladed instrument, usually a knife. penetrating the body. Stab wounds to the trunk must always be treated seriously because of the danger of injury to vital organs and life-threatening internal bleeding.

GUNSHOT WOUND
This type of wound is caused by a bullet Or missile being driven into or through the body. causing serious internal injury and sucking in clothing and contaminants from the air. The entry wound may be small and neat; any exit wound may be large and ragged.